Time is Muscle
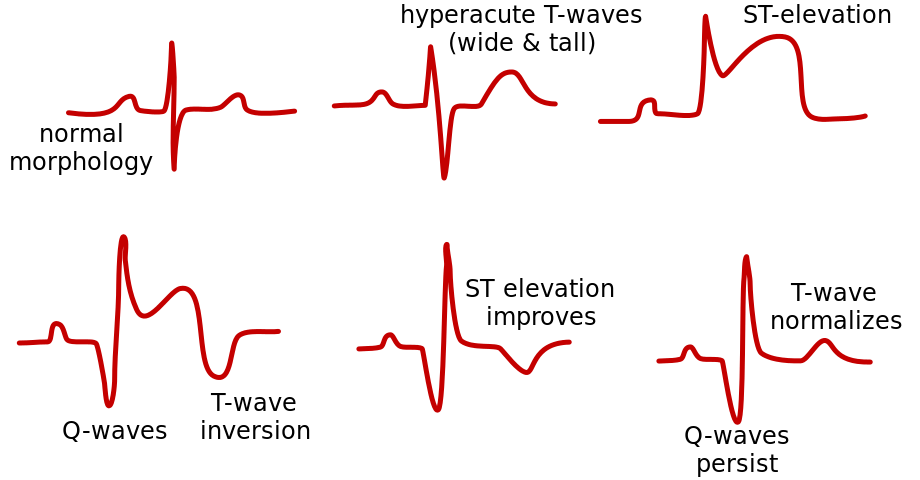
Delivering continuous ST-segment monitoring for those at risk of myocardial infarction can provide a dynamic approach to cardiac monitoring. It picks up changes in the ST-segment. This can supplement continuous bedside ECG monitoring. It can also supplement static 12 lead ECG. Additionally, it aids in monitoring the trend of cardiac enzymes such as Troponin, CK, CK-MB.
This is not new technology, its been around since the mid-1980s. Check out the resources below on the theory. Learn how to set up for monitoring. Find out the best lead for monitoring a suspected occluded coronary artery for ischaemia detection.
ST and STEMI Maps
Keywords: ST Elevation; J-Point; Myocardial Infarction; AMI; STEMI; NSTEMI
Resources
American Nurse. (2007). Saving lives with continuous ST-segment monitoring.
Sangkachand, P., Sarosario, B., & Funk, M. (2011). Continuous ST-segment monitoring: nurses’ attitudes, practices, and quality of patient care. American Journal of Critical Care, 20(3), 226-238.
Sandau, K. E., & Smith, M. (2009). Continuous ST-segment monitoring: protocol for practice. Critical care nurse, 29(4), 39-49.
Leeper, B. (2003). Continuous ST-segment monitoring. AACN Advanced Critical Care, 14(2), 145-154.
GE Healthcare. (2020). An Introduction to 12-lead ST Monitoring.
GE Healthcare. (2020). ST-Segment Monitoring: Benefits, Barriers, and Pathways to Acceptance.
Note: This post is not sponsored or endorsed by any products or companies. It is purely focused on understanding monitoring technology. Additionally, it aims to potentially enhance the level of care delivered in acute coronary care situations. Please share any other monitoring methods or technologies in the comment section below.
Leave a Reply